Premium Natural Indigo Dye for Authentic Textile Crafting and Dyeing Projects
The Allure of High-Quality True Indigo Dye
The world of textiles and dyes is rich with history, culture, and artistry. Among the myriad of colors that artisans have cherished throughout the ages, true indigo dye holds a special place. Recognized for its deep, vibrant blue hue, true indigo, particularly from the plant Indigofera tinctoria, is not just a color; it is a symbol of tradition, craftsmanship, and natural beauty. In this article, we will explore the fascinating journey of true indigo dye, its production processes, its cultural significance, and the benefits of using high-quality indigo in contemporary applications.
The Rich History of Indigo Dyeing
The use of indigo dye dates back thousands of years, with evidence of its use found in ancient civilizations such as Egypt, India, Japan, and the Americas. The dye is derived from the indigo plant, which has been cultivated specifically for its dyeing properties. In India, indigo has been a part of the textile tradition for centuries, often used to dye cotton fabrics. The Japanese have their own indigo-dyeing techniques, known as shibori, which involve intricate folding and binding to create beautiful patterns. Every region has its unique methods and artistic expressions, demonstrating indigo's global significance and enduring appeal.
Production of High-Quality Indigo
High-quality true indigo dye is typically obtained through a multi-step process that requires careful handling of the indigo plant. The leaves of the Indigofera tinctoria plant undergo fermentation, which converts the indican in the leaves into indigo dye. This fermentation, often initiated by adding water and sometimes using specific enzymes, allows for the extraction of a pigment that is almost insoluble in water. The resultant product is a deep blue pigment that can be used in various applications.
The quality of the dye is influenced by several factors, including the age of the plant, the specific conditions in which it is grown, and the fermentation process used. High-quality true indigo is typically characterized by its vibrant hue, ability to create rich layers of color, and excellent lightfastness. Artisans often seek out the finest indigo for traditional dyeing techniques, as it enhances the beauty and longevity of their textiles.
Cultural Significance
high quality true indigo dye
Indigo dyeing is not merely a craft; it is imbued with cultural significance. In many societies, the process of dyeing with indigo has traditional rituals and methods that have been passed down through generations. For example, in West Africa, indigo dyeing is often associated with cultural identity and communal work. In India’s Gujarat region, certain patterns and techniques can signify the wearer's social status or regional affiliation.
These cultural ties have given rise to modern movements that aim to preserve traditional indigo dyeing methods. As consumers become more conscious of the impact of fashion on the environment, there's a growing appreciation for sustainable practices like natural dyeing. High-quality true indigo dye serves as a valuable alternative to synthetic dyes, which can be harmful to both the environment and human health.
Benefits of True Indigo in Contemporary Use
In contemporary textile production, the revival of true indigo dye is welcomed by designers and consumers alike. High-quality indigo offers several advantages
1. Sustainability True indigo is derived from natural sources, making it an environmentally-friendly option. The production processes can often be implemented on a small scale, benefiting local economies and reducing the carbon footprint associated with synthetic dye production.
2. Health and Safety Unlike synthetic dyes, which may contain harmful chemicals, true indigo is safe for use on textiles meant for direct skin contact. This assures consumers of the safety and quality of the products they purchase.
3. Aesthetic Appeal The rich, deep blue of high-quality indigo dye is timeless and versatile. It lends itself well to various applications — from fashion to home décor — allowing for creative expression in numerous forms.
In conclusion, high-quality true indigo dye is more than just a color; it is a cultural artifact, a sustainable practice, and a canvas for artistic expression. Its deep roots in history, combined with modern appreciation for natural and safe dyes, position indigo as not only a staple in the textile industry but also as a symbol of heritage and craftsmanship that continues to inspire generations. As we look to the future of fashion and textile production, true indigo dye will undoubtedly remain an essential player, bridging the gap between tradition and modernity.
-
The Timeless Art of Denim Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Rise of Sulfur Dyed Denim
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Rich Revival of the Best Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Enduring Strength of Sulphur Black
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Ancient Art of Chinese Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Industry Power of Indigo
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Black Sulfur is Leading the Next Wave
NewsJul.01,2025

Sulphur Black
1.Name: sulphur black; Sulfur Black; Sulphur Black 1;
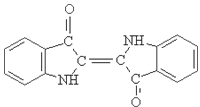
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C6H4N2O5
4.CAS No.: 1326-82-5
5.HS code: 32041911
6.Product specification:Appearance:black phosphorus flakes; black liquid

Bromo Indigo; Vat Bromo-Indigo; C.I.Vat Blue 5
1.Name: Bromo indigo; Vat bromo-indigo; C.I.Vat blue 5;
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C16H6Br4N2O2
4.CAS No.: 2475-31-2
5.HS code: 3204151000 6.Major usage and instruction: Be mainly used to dye cotton fabrics.

Indigo Blue Vat Blue
1.Name: indigo blue,vat blue 1,
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C16H10N2O2
4.. CAS No.: 482-89-3
5.Molecule weight: 262.62
6.HS code: 3204151000
7.Major usage and instruction: Be mainly used to dye cotton fabrics.

