black indigo dye product
The Allure of Black Indigo Dye A Deep Dive into Tradition and Modern Applications
Indigo dyeing is a centuries-old craft that has captivated cultures around the world. Among the various shades of indigo, black indigo stands out for its rich depth and versatility. This article explores the history, production, and modern applications of black indigo dye, showcasing its enduring appeal and significance in both traditional craftsmanship and contemporary fashion.
Historical Significance
Indigo dyeing dates back thousands of years, with evidence of its use found in ancient civilizations, including Egypt, India, and China. The depth of the blue hue was highly prized, making indigo a valuable commodity in trade. Black indigo, derived from the same plant, the indigofera, is created through a fermentation process that yields a darker, more intense color. Historically, black indigo was commonly used in textiles, creating garments that were not only visually stunning but also durable and resistant to fading.
Production Process
The process of producing black indigo dye is intricate and requires a blend of traditional expertise and modern techniques. The primary source of the dye is the leaves of the indigo plant. They are harvested, dried, and then fermented in a process that can take several weeks. During fermentation, the chemical compounds in the leaves are broken down, resulting in a thick, dark liquid that contains the indigo dye. The fabric is then dipped multiple times in this dye bath, which allows for deeper saturation and richer color.
One of the fascinating aspects of the dyeing process is its environmentally friendly nature. Natural indigo is biodegradable, and many artisans continue to use traditional methods passed down through generations. However, modern advancements have also introduced synthetic alternatives that mimic the appearance of black indigo while improving color consistency and reducing production time.
Cultural Impact
black indigo dye product
Black indigo dye is steeped in cultural significance, particularly in countries like Japan, where it is employed in the art of shibori, a tie-dye technique that creates stunning patterns through meticulous folding and binding. In West Africa, traditional indigo dyeing techniques are integral to the cultural identity of various ethnic groups, with intricate designs that tell stories and convey heritage.
The appeal of black indigo has transcended cultural boundaries and found its place in the global fashion industry. Designers today are increasingly drawn to the unique aesthetic of indigo-dyed fabrics, incorporating them into collections that celebrate sustainable and artisanal practices. The resurgence of interest in eco-friendly fashion has further boosted the popularity of natural indigo, as consumers seek to connect with tradition and authenticity.
Modern Applications
Beyond fashion, black indigo dye has found applications in various creative fields. Artists and designers utilize black indigo in various media, from textiles to home decor. Its versatility allows for experimentation with patterns, textures, and techniques that captivate audiences and breathe new life into everyday objects.
In addition to its aesthetic value, the use of natural indigo is gaining recognition for its potential environmental benefits. Unlike synthetic dyes, which can be harmful to the ecosystem, natural indigo dyeing processes often employ sustainable practices that minimize waste and reduce environmental impact.
Conclusion
Black indigo dye is more than just a color; it embodies a rich history and a cultural narrative that spans continents and centuries. Its production, steeped in tradition, showcases the craft of artisans dedicated to preserving this age-old technique. As the world continues to embrace sustainable choices, the allure of black indigo dye is likely to endure, captivating new generations and bridging the gap between past and present. From its deep-rooted history to its modern applications, black indigo remains a timeless symbol of creativity and cultural heritage.
-
The Timeless Art of Denim Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Rise of Sulfur Dyed Denim
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Rich Revival of the Best Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Enduring Strength of Sulphur Black
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Ancient Art of Chinese Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Industry Power of Indigo
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Black Sulfur is Leading the Next Wave
NewsJul.01,2025

Sulphur Black
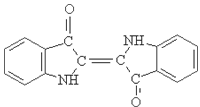
1.Name: sulphur black; Sulfur Black; Sulphur Black 1;
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C6H4N2O5
4.CAS No.: 1326-82-5
5.HS code: 32041911
6.Product specification:Appearance:black phosphorus flakes; black liquid

Bromo Indigo; Vat Bromo-Indigo; C.I.Vat Blue 5
1.Name: Bromo indigo; Vat bromo-indigo; C.I.Vat blue 5;
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C16H6Br4N2O2
4.CAS No.: 2475-31-2
5.HS code: 3204151000 6.Major usage and instruction: Be mainly used to dye cotton fabrics.

Indigo Blue Vat Blue
1.Name: indigo blue,vat blue 1,
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C16H10N2O2
4.. CAS No.: 482-89-3
5.Molecule weight: 262.62
6.HS code: 3204151000
7.Major usage and instruction: Be mainly used to dye cotton fabrics.

