Exploring the Rich History and Artistry of Chinese Indigo Dyeing Techniques
The Journey of China Indigo A Cultural and Economic Legacy
Indigo, often recognized for its deep blue hues, has a rich history intertwined with the cultural and economic landscapes of China. This natural dye, derived from the plants of the genus Indigofera, has not only colored textiles but has also played a significant role in trade, art, and tradition throughout the centuries.
Historical Significance
The use of indigo in China dates back over two thousand years. Historical records indicate that indigo-dyed fabrics were highly valued in the Han Dynasty (206 BC – 220 AD) and were often used in ceremonial contexts. The dye's ability to produce vibrant shades of blue made it a favorite among artisans and dignitaries alike. With the Silk Road fostering trade routes connecting China to the West, indigo began to circulate globally, solidifying its status as a coveted commodity.
During the Tang (618-907 AD) and Song (960-1279 AD) Dynasties, Chinese indigo reached new heights in terms of production and popularity. The introduction of new dyeing techniques allowed artisans to create intricate designs that showcased the beauty of the deep blue color, further embedding indigo into the fabric of Chinese culture.
Economic Impact
The cultivation and trade of indigo significantly contributed to local economies, particularly in areas like Jiangsu, Zhejiang, and Guangxi provinces, where the climate and soil conditions are favorable for the Indigofera plant. The indigo industry provided livelihoods for countless families, fostering agricultural practices that went hand in hand with craftsmanship.
As trade evolved, so did the methods of production. The traditional fermentation process, which involves soaking the leaves of the indigo plant in water to create a dye bath, has been passed down through generations. However, the introduction of synthetic dyes in the 20th century posed a challenge to the natural indigo industry, leading to a decline in its popularity.
china indigo on
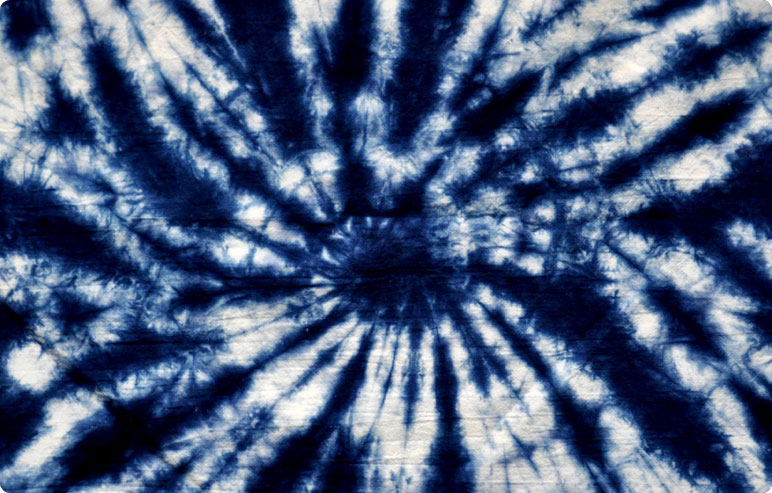
Revival and Modern Significance
In recent years, there has been a renewed interest in natural dyes, including indigo, as part of a global trend towards sustainable and eco-friendly practices. Environmental concerns and a growing appreciation for artisanal craftsmanship have spurred a revival of traditional indigo dyeing techniques. This resurgence is not only about preserving history; it also speaks to a desire for authenticity and a connection to nature in an increasingly industrialized world.
Today, Chinese indigo is not just a relic of the past but a vibrant part of contemporary fashion and design. Designers and brands worldwide are incorporating indigo into their collections, celebrating its rich history and aesthetic appeal. Organic indigo farms and workshops are sprouting across China, where artisans blend ancient techniques with modern sensibilities to create unique products ranging from clothing to home decor.
Cultural Symbolism
Indigo dye carries with it deep cultural significance in various Chinese communities. In some traditions, blue symbolizes protection and is believed to ward off evil spirits. It is often used in traditional costumes during festivals and significant life events, binding individuals to their cultural heritage. The revival of indigo not only highlights its aesthetic qualities but also reinforces connections to tradition, identity, and community.
Conclusion
The journey of China indigo from ancient times to the modern era encapsulates the essence of cultural resilience and economic evolution. As indigo continues to weave its story through the fabric of Chinese society, it stands as a testament to the enduring legacy of this exquisite dye. With its revival in sustainable practices and contemporary design, indigo remains a vibrant symbol of China's artistic heritage, bridging the gap between past and present. As we celebrate this timeless dye, we find ourselves not just preserving history but also cultivating a deeper appreciation for the artistry and traditions that it represents.
-
The Timeless Art of Denim Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Rise of Sulfur Dyed Denim
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Rich Revival of the Best Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Enduring Strength of Sulphur Black
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Ancient Art of Chinese Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Industry Power of Indigo
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Black Sulfur is Leading the Next Wave
NewsJul.01,2025

Sulphur Black
1.Name: sulphur black; Sulfur Black; Sulphur Black 1;
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C6H4N2O5
4.CAS No.: 1326-82-5
5.HS code: 32041911
6.Product specification:Appearance:black phosphorus flakes; black liquid

Bromo Indigo; Vat Bromo-Indigo; C.I.Vat Blue 5
1.Name: Bromo indigo; Vat bromo-indigo; C.I.Vat blue 5;
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C16H6Br4N2O2
4.CAS No.: 2475-31-2
5.HS code: 3204151000 6.Major usage and instruction: Be mainly used to dye cotton fabrics.

Indigo Blue Vat Blue
1.Name: indigo blue,vat blue 1,
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C16H10N2O2
4.. CAS No.: 482-89-3
5.Molecule weight: 262.62
6.HS code: 3204151000
7.Major usage and instruction: Be mainly used to dye cotton fabrics.

