china indigo plants for dyeing
Indigo dyeing has a rich history that dates back thousands of years, particularly in China, where the cultivation of indigo plants has been an integral part of textile production. The traditional methods of dyeing with indigo not only reflect the ingenuity of ancient cultures but also showcase the beauty of natural colors derived from plants.
Indigo dyeing has a rich history that dates back thousands of years, particularly in China, where the cultivation of indigo plants has been an integral part of textile production
. The traditional methods of dyeing with indigo not only reflect the ingenuity of ancient cultures but also showcase the beauty of natural colors derived from plants.Indigo dyeing in China is not merely a craft; it is an art form that reflects regional identities and traditions. Various provinces have developed their unique styles and techniques, resulting in a vibrant tapestry of indigo-dyed textiles. For instance, the Miao and Yi ethnic groups in southwestern China have incorporated indigo dyeing into their cultural practices, creating intricate patterns and motifs that hold significant cultural meanings. The blue hues of indigo fabrics often symbolize protection, wealth, and prosperity within these communities.
china indigo plants for dyeing
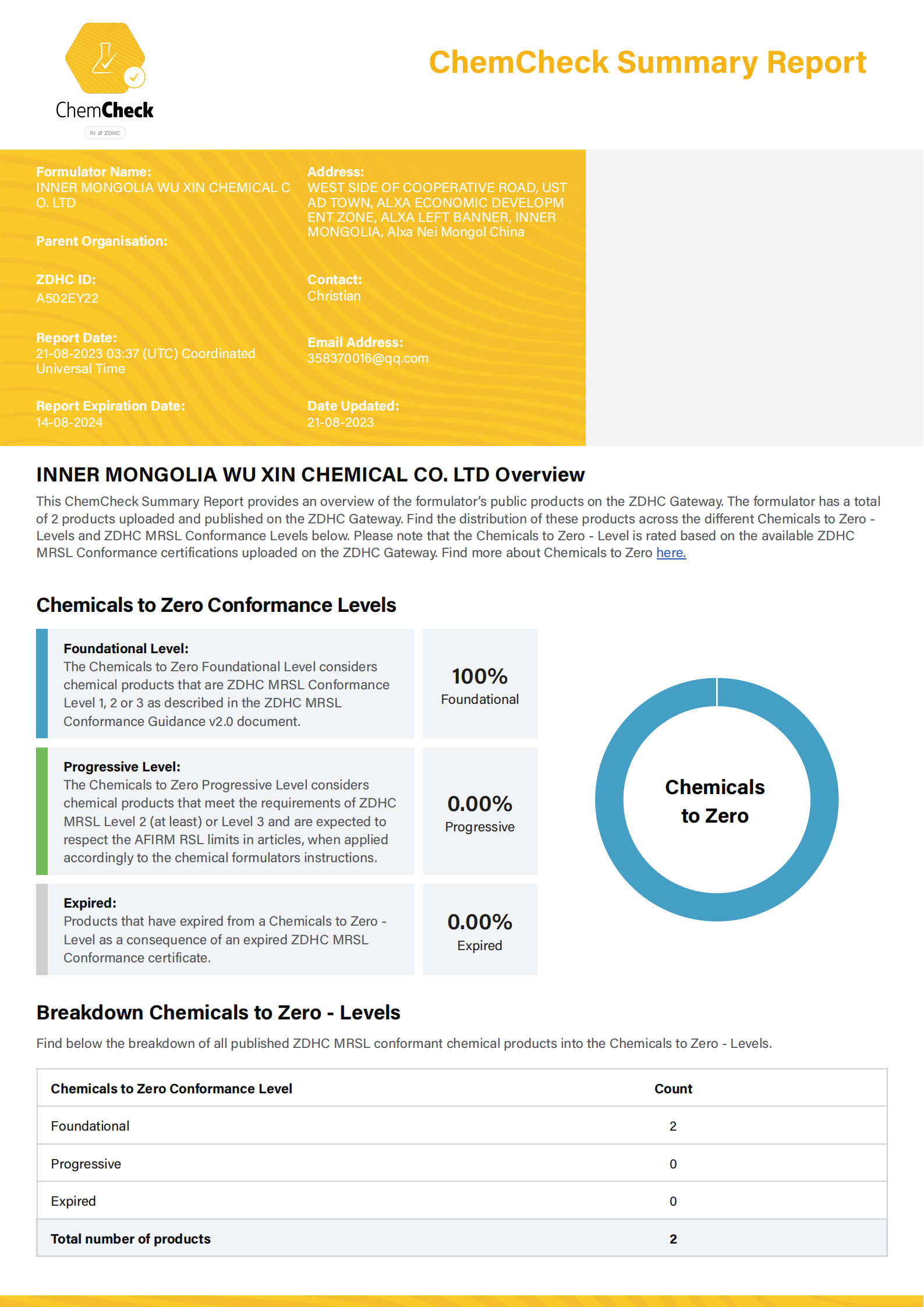
In recent years, the popularity of indigo dyeing has experienced a resurgence. As consumers become more aware of sustainable and environmentally friendly practices, natural dyes are making a comeback in the fashion industry. Artisans and designers are rediscovering traditional techniques and reinterpreting them for modern aesthetics. This revival not only supports local economies but also preserves the rich cultural heritage associated with indigo dyeing.
Moreover, the use of indigo dye has expanded beyond textiles into other areas, including home decor and artisanal crafts. The deep, vibrant blues offer a stunning contrast to neutral palettes, making indigo-dyed items highly sought after in contemporary design.
In conclusion, the indigo plants grown in China for dyeing represent not just a source of color but also a deep cultural legacy. Their rich history, combined with modern-day appreciation for natural dyes, highlights the enduring significance of indigo in both traditional and contemporary contexts. As we move towards more sustainable practices in the fashion and craft industries, the timeless beauty of indigo will continue to thrive, connecting the past to the present.
-
The Timeless Art of Denim Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Rise of Sulfur Dyed Denim
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Rich Revival of the Best Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Enduring Strength of Sulphur Black
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Ancient Art of Chinese Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Industry Power of Indigo
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Black Sulfur is Leading the Next Wave
NewsJul.01,2025

Sulphur Black
1.Name: sulphur black; Sulfur Black; Sulphur Black 1;
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C6H4N2O5
4.CAS No.: 1326-82-5
5.HS code: 32041911
6.Product specification:Appearance:black phosphorus flakes; black liquid

Bromo Indigo; Vat Bromo-Indigo; C.I.Vat Blue 5
1.Name: Bromo indigo; Vat bromo-indigo; C.I.Vat blue 5;
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C16H6Br4N2O2
4.CAS No.: 2475-31-2
5.HS code: 3204151000 6.Major usage and instruction: Be mainly used to dye cotton fabrics.

Indigo Blue Vat Blue
1.Name: indigo blue,vat blue 1,
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C16H10N2O2
4.. CAS No.: 482-89-3
5.Molecule weight: 262.62
6.HS code: 3204151000
7.Major usage and instruction: Be mainly used to dye cotton fabrics.

