Japanese Indigo Fabric Production and Its Cultural Significance in Textile Craftsmanship
Japanese indigo cloth, known as ai in Japanese, has a rich history and a significant cultural value that dates back centuries. The production of indigo dyeing has been integral to Japan's textile industry, particularly in regions such as Tokushima and Okayama, where the craft has been perfected over generations.
Japanese indigo cloth, known as ai in Japanese, has a rich history and a significant cultural value that dates back centuries
. The production of indigo dyeing has been integral to Japan's textile industry, particularly in regions such as Tokushima and Okayama, where the craft has been perfected over generations.The processes involved in creating indigo cloth are labor-intensive and require great skill. Artisans, or shokunin, meticulously grow indigo plants, harvest them, and then ferment the leaves to produce a dye. This dyeing technique is unique due to its ability to create rich, layered shades of blue, which can be achieved through repeated dyeing. Each piece of fabric undergoes careful craftsmanship, resulting in textiles that are not only functional but also visually stunning.
japanese indigo cloth factories
Japanese indigo cloth factories focus on preserving traditional methods while also embracing modern innovation. Many craftsmen are now integrating contemporary designs and techniques into their work, leading to a resurgence in popularity among younger generations. This revival is crucial for sustaining the craft, as it attracts new interest and appreciation for indigo textiles.
In recent years, there has also been a growing trend towards sustainable fashion. Japanese indigo dyeing is often highlighted for its eco-friendly properties, as the indigo plant is a natural resource that offers a biodegradable alternative to synthetic dyes. Factory practices are also increasingly emphasizing sustainable methods, promoting ethical production within the industry.
Overall, Japanese indigo cloth factories represent a blend of tradition and modernity. The commitment to preserving age-old techniques while adapting to contemporary demands reflects the resilience of this art form. As the world becomes more conscious of sustainability and ethical craftsmanship, the allure of Japanese indigo continues to grow, ensuring that this beautiful textile remains relevant in today’s fashion landscape.
-
The Timeless Art of Denim Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Rise of Sulfur Dyed Denim
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Rich Revival of the Best Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Enduring Strength of Sulphur Black
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Ancient Art of Chinese Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Industry Power of Indigo
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Black Sulfur is Leading the Next Wave
NewsJul.01,2025

Sulphur Black
1.Name: sulphur black; Sulfur Black; Sulphur Black 1;
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C6H4N2O5
4.CAS No.: 1326-82-5
5.HS code: 32041911
6.Product specification:Appearance:black phosphorus flakes; black liquid

Bromo Indigo; Vat Bromo-Indigo; C.I.Vat Blue 5
1.Name: Bromo indigo; Vat bromo-indigo; C.I.Vat blue 5;
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C16H6Br4N2O2
4.CAS No.: 2475-31-2
5.HS code: 3204151000 6.Major usage and instruction: Be mainly used to dye cotton fabrics.

Indigo Blue Vat Blue
1.Name: indigo blue,vat blue 1,
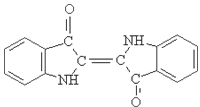
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C16H10N2O2
4.. CAS No.: 482-89-3
5.Molecule weight: 262.62
6.HS code: 3204151000
7.Major usage and instruction: Be mainly used to dye cotton fabrics.

