Manufacturers of High-Quality Blue Indigo Powder for Various Applications
The World of Blue Indigo Powder Insights into Manufacturers and Their Impact
In recent years, blue indigo powder has gained significant popularity, not just for its rich color but also for its cultural heritage and ecological benefits. Derived from the indigo plant, this natural dye has been used for centuries in various applications, ranging from textiles to cosmetics. As the demand for sustainable and organic products continues to rise, manufacturers of blue indigo powder play a pivotal role in preserving traditional practices while meeting the expectations of modern consumers.
The Process of Indigo Powder Production
The production of blue indigo powder is a meticulous process that involves several stages. It begins with the cultivation of the indigo plant, primarily Indigofera tinctoria. This plant thrives in tropical and subtropical climates and has been cultivated in regions like India, Africa, and Southeast Asia for generations. The leaves are harvested, and the key ingredient—indican—is extracted through a fermentation process. The leaves are soaked in water, where bacteria break down the indican, releasing indigo dye.
After fermentation, the indigo precipitates out of the solution and is filtered. The resulting paste is then dried and ground into a fine powder, ready for packaging and distribution. This process not only preserves the natural properties of indigo but also keeps the production as eco-friendly as possible.
Sustainability and Ethical Practices
With a growing global emphasis on sustainability, many blue indigo powder manufacturers are adopting eco-friendly practices
. From using organic farming methods to minimize chemical use to implementing fair trade practices that support local farmers, these manufacturers are showcasing a commitment to the environment and social responsibility.Sustainable practices are increasingly important as consumers seek products that align with their values. For example, some manufacturers have established direct relationships with farmers, ensuring they receive fair compensation for their work while promoting sustainable agricultural practices. This level of cooperation supports local economies and fosters community development.
blue indigo powder manufacturers
The Market Demand for Natural Dyes
The resurgence of interest in natural dyes, particularly indigo, can be attributed to several factors. As consumers become more aware of the environmental impact of synthetic dyes, many are turning to natural alternatives. This shift is evident in the fashion industry, where brands are increasingly incorporating indigo-dyed fabrics into their collections. The unique shades and patterns created through indigo dyeing are celebrated for their authenticity and artisanal qualities.
Moreover, the beauty and skincare industry has also recognized the potential of blue indigo powder. With its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, indigo has found its way into various cosmetic products, from hair dyes to face masks. Manufacturers are thus diversifying their product lines to cater to this expanding market, capitalizing on the intersection of natural health trends and aesthetic appeal.
Challenges Facing Indigo Powder Manufacturers
Despite the growing demand for blue indigo powder, manufacturers face several challenges. Climate change poses a significant threat to the cultivation of indigo plants, as shifting weather patterns can affect crop yields. Manufacturers must adapt their practices to mitigate these impacts while ensuring product quality remains high.
Additionally, competition from synthetic dyes remains fierce. While natural dyes are increasingly favored for their environmental benefits, synthetic alternatives offer consistency, vibrant colors, and lower costs. Overcoming this challenge will require a concerted effort from manufacturers to educate consumers about the benefits of indigo and the significance of supporting sustainable practices.
Conclusion
Blue indigo powder represents more than just a vibrant hue; it is a symbol of cultural heritage, sustainability, and ethical manufacturing. As the demand for natural products continues to rise, manufacturers have the opportunity to lead the way in fostering both environmental stewardship and social responsibility. By embracing sustainable practices and fostering connections within local communities, they can not only preserve ancient traditions but also meet the evolving needs of modern consumers. The world of blue indigo powder is a testament to the harmonious blend of nature and industry, showcasing how tradition can thrive amidst innovation.
-
The Timeless Art of Denim Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Rise of Sulfur Dyed Denim
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Rich Revival of the Best Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Enduring Strength of Sulphur Black
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Ancient Art of Chinese Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Industry Power of Indigo
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Black Sulfur is Leading the Next Wave
NewsJul.01,2025

Sulphur Black
1.Name: sulphur black; Sulfur Black; Sulphur Black 1;
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C6H4N2O5
4.CAS No.: 1326-82-5
5.HS code: 32041911
6.Product specification:Appearance:black phosphorus flakes; black liquid

Bromo Indigo; Vat Bromo-Indigo; C.I.Vat Blue 5
1.Name: Bromo indigo; Vat bromo-indigo; C.I.Vat blue 5;
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C16H6Br4N2O2
4.CAS No.: 2475-31-2
5.HS code: 3204151000 6.Major usage and instruction: Be mainly used to dye cotton fabrics.

Indigo Blue Vat Blue
1.Name: indigo blue,vat blue 1,
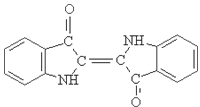
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C16H10N2O2
4.. CAS No.: 482-89-3
5.Molecule weight: 262.62
6.HS code: 3204151000
7.Major usage and instruction: Be mainly used to dye cotton fabrics.

