Exploring Sustainable Indigo Dyeing Practices in India's Textile Industry
The Allure of Indigo Dyeing in India A Cultural and Economic Journey
Indigo dyeing has been an integral part of Indian textile heritage for centuries, crafting a narrative that blends tradition, culture, and economic significance. The deep, rich blue of indigo, derived from the leaves of the Indigofera plant, has captivated artisans and consumers alike, making it one of the most sought-after colors in textile production. As global interest in sustainable and artisanal products surges, buying indigo-dyed textiles in India presents an opportunity to engage in a tradition that is as sustainable as it is beautiful.
The Historical Significance of Indigo in India
The roots of indigo dyeing in India trace back over 5,000 years, with historical accounts highlighting its use in ancient civilizations. The significance of indigo, both culturally and economically, became particularly pronounced during the colonial era when the British sought to monopolize the lucrative indigo trade. The blue dye became symbolic of resistance and identity for many Indian communities, leading to movements that sought to protect indigenous practices from colonial exploitation.
Today, indigo dyeing continues to thrive in regions like Gujarat and Rajasthan, where artisans employ traditional techniques passed down through generations. The process involves farming the indigo plants, fermenting the leaves, and meticulously dyeing textiles, resulting in variations that showcase the skill and artistry involved. Each piece tells a story, reflecting the rich heritage of its maker and the community it represents.
The Environmental Impact and Sustainability
In an age where sustainable fashion is increasingly valued, indigo dyeing stands out as an eco-friendly alternative to synthetic dyes. Traditional indigo dyeing processes use natural, biodegradable materials, making them less harmful to the environment. Many artisans incorporate organic farming practices, ensuring that their methods do not contribute to soil degradation or water pollution, issues often associated with industrial dyeing processes.
In recent years, the global demand for ethically sourced and environmentally friendly products has given a new lease of life to indigo dyeing
. By choosing to buy indigo-dyed textiles from India, consumers can support sustainable practices that prioritize the planet while preserving artisanal heritage.buy indigo dyeing in india
Economic Empowerment for Artisans
Buying indigo-dyed products also plays a crucial role in empowering local artisans and their communities. Many artisans rely on this craft as their primary source of income. When consumers opt for authentic indigo textiles, they contribute directly to the livelihoods of these craftsmen and their families, fostering economic stability and community development.
Moreover, various initiatives aim to promote fair trade practices, ensuring that artisans receive a fair wage for their labor and skills. By choosing ethically made indigo products, consumers can play a part in alleviating poverty in these communities and promoting social sustainability.
The Contemporary Appeal of Indigo
The unique aesthetic appeal of indigo dyeing has transcended cultural and geographical boundaries. From fashion runways to home decor, indigo-dyed fabrics are celebrated for their versatility and timeless beauty. The deep hues, intricate patterns, and texture of indigo textiles can elevate any wardrobe or living space, making them a favored choice among designers and consumers alike.
As a result, buying indigo-dyed textiles in India has become more than just a shopping experience; it is a chance to participate in a rich cultural tradition while making conscious choices that reflect a commitment to sustainability and community support.
Conclusion
In summary, the act of purchasing indigo-dyed textiles from India is a journey into a historical and cultural tapestry rich with significance. By choosing these products, consumers can engage in ethical consumption, support local artisans, and celebrate the timeless beauty of indigo dyeing. Each indigo-dyed piece ultimately tells a story—a story of resilience, artistry, and the continuing legacy of India’s vibrant textile heritage.
-
The Timeless Art of Denim Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Rise of Sulfur Dyed Denim
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Rich Revival of the Best Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Enduring Strength of Sulphur Black
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Ancient Art of Chinese Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Industry Power of Indigo
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Black Sulfur is Leading the Next Wave
NewsJul.01,2025

Sulphur Black
1.Name: sulphur black; Sulfur Black; Sulphur Black 1;
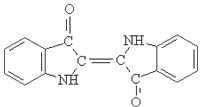
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C6H4N2O5
4.CAS No.: 1326-82-5
5.HS code: 32041911
6.Product specification:Appearance:black phosphorus flakes; black liquid

Bromo Indigo; Vat Bromo-Indigo; C.I.Vat Blue 5
1.Name: Bromo indigo; Vat bromo-indigo; C.I.Vat blue 5;
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C16H6Br4N2O2
4.CAS No.: 2475-31-2
5.HS code: 3204151000 6.Major usage and instruction: Be mainly used to dye cotton fabrics.

Indigo Blue Vat Blue
1.Name: indigo blue,vat blue 1,
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C16H10N2O2
4.. CAS No.: 482-89-3
5.Molecule weight: 262.62
6.HS code: 3204151000
7.Major usage and instruction: Be mainly used to dye cotton fabrics.

