Exploring the Rich History and Uses of Blue Indigo Dye in Textiles
The Rich History and Cultural Significance of Blue Indigo Dye
Indigo dye, with its deep, rich hues ranging from royal blue to soft indigo, holds a significant place in the history of textiles and art. Known for its unique ability to resist fading even in intense sunlight, indigo has been utilized across cultures for centuries, making it one of the oldest dyes known to humanity.
The use of indigo can be traced back over 6,000 years to ancient civilizations in regions like India, Egypt, and Mesopotamia. These early applications of the dye were not only functional but also symbolic. In many cultures, blue represented the heavens and was associated with deities. For instance, in ancient Egypt, blue dyes were used in funerary clothes to convey a sense of peace and protection for the deceased in the afterlife.
The Rich History and Cultural Significance of Blue Indigo Dye
The indigo dye trade flourished in the 16th and 17th centuries. European demand for blue textiles surged, leading to the establishment of indigo plantations in the Americas and the Caribbean. However, this growth came at a significant cost, particularly through the exploitation of enslaved individuals who worked under brutal conditions in these plantations. The history of indigo is thus intertwined with themes of labor, colonialism, and economic exploitation.
blue indigo dye
As time progressed, the industrial revolution brought synthetic alternatives to natural indigo dye, leading to a decline in its popularity. However, the unique qualities of natural indigo have revived interest in traditional dyeing methods. Today, artisans and designers are increasingly turning back to natural indigo, appreciating its ecological benefits and cultural significance. Natural indigo production is often viewed through a sustainable lens, as it can be cultivated without harmful chemicals, overuse of water, or the ecological consequences associated with synthetic dyes.
Indigo's versatility and beauty have transcended fashion. Artists and designers now utilize it in home decor, visual arts, and innovative textiles. Blue indigo hues can be seen in contemporary art installations and fashion collections that pay homage to traditional techniques while melding them with modern aesthetics. This revival is an essential step in recognizing and respecting the cultural heritage tied to indigo dyeing.
Moreover, in recent years, indigo dyeing workshops have sprung up in urban areas, allowing people to engage directly with this ancient craft. These workshops not only provide a platform for individuals to learn about the dyeing process but also create awareness about the importance of preserving traditional methodologies. Participants witness firsthand how different techniques, from fermentation to various application methods, result in a spectrum of indigo shades and patterns.
In conclusion, blue indigo dye is not merely a color; it is a profound symbol of history, culture, and resilience. Its journey from ancient civilizations to contemporary artisan practices underscores the intricate relationships between art, identity, and sustainability. As we adopt responsible practices in our quest for beauty, indigo remains a potent reminder of our shared humanity and the cultural tapestries that bind us together. The continued appreciation for blue indigo dye reflects our commitment to honoring tradition while innovating for a sustainable future.
-
The Timeless Art of Denim Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Rise of Sulfur Dyed Denim
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Rich Revival of the Best Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Enduring Strength of Sulphur Black
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Ancient Art of Chinese Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Industry Power of Indigo
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Black Sulfur is Leading the Next Wave
NewsJul.01,2025

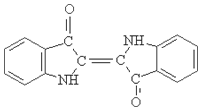
Sulphur Black
1.Name: sulphur black; Sulfur Black; Sulphur Black 1;
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C6H4N2O5
4.CAS No.: 1326-82-5
5.HS code: 32041911
6.Product specification:Appearance:black phosphorus flakes; black liquid

Bromo Indigo; Vat Bromo-Indigo; C.I.Vat Blue 5
1.Name: Bromo indigo; Vat bromo-indigo; C.I.Vat blue 5;
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C16H6Br4N2O2
4.CAS No.: 2475-31-2
5.HS code: 3204151000 6.Major usage and instruction: Be mainly used to dye cotton fabrics.

Indigo Blue Vat Blue
1.Name: indigo blue,vat blue 1,
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C16H10N2O2
4.. CAS No.: 482-89-3
5.Molecule weight: 262.62
6.HS code: 3204151000
7.Major usage and instruction: Be mainly used to dye cotton fabrics.

