famous indigo black powder
The Allure of Famous Indigo Black Powder A Journey Through History and Utility
Indigo, a hue steeped in history, has long been associated with luxury, artistry, and craftsmanship. Among the various manifestations of this revered color is indigo black powder, a unique blend that has captured the attention of artisans, historians, and chemists alike. This article delves into the significance and uses of famous indigo black powder, tracing its roots and exploring its cultural impact.
Historically, indigo dyeing dates back thousands of years, with evidence of its use in ancient civilizations from Egypt to India. The vibrant blue pigment derives from the leaves of the indigo plant, primarily Indigofera tinctoria. While the blue indigo dye has dominated the narrative, the creation of indigo black powder represents a fascinating evolution in the utilization of indigo. This transformation typically involves a combination of indigo with other elements, resulting in a rich black that marries the hues of blue with darker shades.
One of the key appeals of indigo black powder lies in its versatility. Artists have embraced it as a pigment in various forms, from traditional painting to modern applications. In the realm of fine arts, indigo black powder serves as an essential color for creating depth and contrast. Its rich, complex shades can evoke a range of emotions, making it an attractive choice for painters seeking to elevate their work.
Moreover, indigo black powder has made significant inroads in the textile industry. From the creation of luxurious fabrics to intricate patterns, the powder not only imparts a distinctive color but also enhances the durability of fabrics. It is commonly used in traditional dyeing practices, especially in regions renowned for their textile craftsmanship, such as Japan, where indigo dyeing techniques have been perfected over centuries. The result is a fabric that is not only visually stunning but also imbued with cultural significance.
famous indigo black powder
The environmental aspect of indigo black powder further elevates its appeal. As society increasingly emphasizes sustainable practices, the use of natural indigo and its derivatives has seen a resurgence. Unlike synthetic dyes, which often contain harmful chemicals, indigo is derived from plants, making it a more eco-friendly alternative. The cultivation and processing of indigo plants can provide economic benefits to farming communities, promoting sustainability and preserving traditions associated with dyeing techniques.
While primarily recognized for its aesthetic qualities, indigo black powder also boasts a rich history in medicinal and spiritual practices. In various cultures, the indigo plant has been attributed with healing properties, making its use prevalent in folk medicine. Some belief systems link indigo to purification and protection, utilizing the pigment in rituals and ceremonies. This dimension of indigo black powder adds layers of meaning, intertwining artistry with spirituality and wellness.
Furthermore, in the art of calligraphy, indigo black powder has become a popular choice among practitioners. Its deep, lustrous finish enhances the beauty of each brushstroke, allowing for a unique expression of creativity. The combination of textured paper and indigo black powder can create a breathtaking contrast, bringing written art to life in ways that few other pigments can match.
While the aesthetic and practical applications of indigo black powder are well-documented, its role in modern culture continues to evolve. Today, designers and artisans breathe new life into this ancient material, finding innovative ways to incorporate it into contemporary practices. From fashion to home décor, indigo black powder has transcended its historical roots, embracing modernity while staying connected to its origin.
In conclusion, famous indigo black powder encapsulates a rich tapestry of history, culture, and artistry. Its multifaceted uses—from vibrant textiles to stunning artworks—speak to its enduring appeal. As we navigate the complexities of modern society, the revival of traditional materials like indigo black powder not only honors the past but also paves the way for a sustainable and artistic future. By reconnecting with these roots, we celebrate not just the color but the stories, traditions, and creative expressions that indigo has inspired across generations.
-
The Timeless Art of Denim Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Rise of Sulfur Dyed Denim
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Rich Revival of the Best Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Enduring Strength of Sulphur Black
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Ancient Art of Chinese Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Industry Power of Indigo
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Black Sulfur is Leading the Next Wave
NewsJul.01,2025

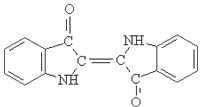
Sulphur Black
1.Name: sulphur black; Sulfur Black; Sulphur Black 1;
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C6H4N2O5
4.CAS No.: 1326-82-5
5.HS code: 32041911
6.Product specification:Appearance:black phosphorus flakes; black liquid

Bromo Indigo; Vat Bromo-Indigo; C.I.Vat Blue 5
1.Name: Bromo indigo; Vat bromo-indigo; C.I.Vat blue 5;
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C16H6Br4N2O2
4.CAS No.: 2475-31-2
5.HS code: 3204151000 6.Major usage and instruction: Be mainly used to dye cotton fabrics.

Indigo Blue Vat Blue
1.Name: indigo blue,vat blue 1,
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C16H10N2O2
4.. CAS No.: 482-89-3
5.Molecule weight: 262.62
6.HS code: 3204151000
7.Major usage and instruction: Be mainly used to dye cotton fabrics.

