indigo organic powder factories
Exploring the World of Indigo Organic Powder Factories
Indigo organic powder, derived from the leaves of the indigo plant, has been celebrated for centuries for its vibrant and deep blue hues. Its applications range from textile dyeing to health supplements, all while promoting sustainable practices. As the demand for natural alternatives to synthetic dyes and harmful additives increases, the role of indigo organic powder factories has never been more crucial.
The process begins with the cultivation of indigo plants, primarily found in regions like India, Madagascar, and Nigeria. These plants thrive in tropical climates and require minimal chemical intervention, making them an ideal crop for organic farming. Once harvested, the leaves undergo a fermentation process designed to extract the indigo pigment. This biotechnological method not only preserves the environmental integrity of the product but also enhances its quality.
Organic indigo powder factories prioritize sustainability throughout their production processes. By relying on traditional methods alongside modern innovations, these facilities minimize waste and energy consumption. For instance, water from the dyeing process can be recycled, while byproducts from the fermentation can be transformed into fertilizer for future crops. Such practices not only reduce the environmental footprint but also contribute to the circular economy, which is becoming increasingly important in today’s manufacturing landscape.
indigo organic powder factories
Quality control is another essential aspect of indigo organic powder production. Factories often implement rigorous testing protocols to ensure that their product meets both quality and safety standards. From monitoring pesticide levels in the raw plants to conducting final tests on the powder itself, these measures guarantee that consumers are receiving a safe and effective product. Labels that proudly display certifications such as USDA Organic or EcoCert help consumers make informed choices.
Furthermore, indigo organic powder has transcended traditional uses. While it has long been celebrated as a natural dye for textiles, it is also gaining traction in the wellness industry. The powder is rich in antioxidants and has been linked to various health benefits, including digestive improvement and skin care. This diversification has sparked interest in new applications and led to the establishment of partnerships between powder manufacturers and product developers, creating a win-win scenario.
In conclusion, indigo organic powder factories play a vital role in the sustainable production of this ancient dye. By embracing eco-friendly practices, adhering to quality standards, and expanding the potential uses of indigo, these manufacturers not only cater to the growing market for natural products but also contribute to environmental conservation. As consumers continue to seek out organic and sustainable options, the future of indigo organic powder appears brighter than ever—a testament to the enduring legacy of this remarkable plant and its myriad applications.
-
The Timeless Art of Denim Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Rise of Sulfur Dyed Denim
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Rich Revival of the Best Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Enduring Strength of Sulphur Black
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Ancient Art of Chinese Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Industry Power of Indigo
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Black Sulfur is Leading the Next Wave
NewsJul.01,2025

Sulphur Black
1.Name: sulphur black; Sulfur Black; Sulphur Black 1;
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C6H4N2O5
4.CAS No.: 1326-82-5
5.HS code: 32041911
6.Product specification:Appearance:black phosphorus flakes; black liquid

Bromo Indigo; Vat Bromo-Indigo; C.I.Vat Blue 5
1.Name: Bromo indigo; Vat bromo-indigo; C.I.Vat blue 5;
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C16H6Br4N2O2
4.CAS No.: 2475-31-2
5.HS code: 3204151000 6.Major usage and instruction: Be mainly used to dye cotton fabrics.

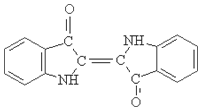
Indigo Blue Vat Blue
1.Name: indigo blue,vat blue 1,
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C16H10N2O2
4.. CAS No.: 482-89-3
5.Molecule weight: 262.62
6.HS code: 3204151000
7.Major usage and instruction: Be mainly used to dye cotton fabrics.

