Leading Manufacturer of High-Quality Indigo Dye for Jeans Production Worldwide
The Evolution of Indigo Dye A Look into Denim's Roots
Indigo dye has been a cornerstone of the textile industry for centuries, particularly in the production of denim. This deep blue dye, derived from the plant Indigofera tinctoria, has a rich history that spans various cultures and continents. The process of creating indigo dye has evolved significantly, influencing not only fashion but also economic and social landscapes.
The Evolution of Indigo Dye A Look into Denim's Roots
The introduction of indigo to the New World marked a significant turning point in its history. In the 17th century, indigo plantations flourished in the American South, where the climate proved ideal for its cultivation. As American colonial demand for blue-dyed fabrics surged, indigo became a major cash crop, leading to economic prosperity for many plantation owners. The resulting garments, particularly jeans made from indigo-dyed denim, became symbols of Americana, embodying both practicality and style.
jeans indigo dye manufacturer
As denim gained popularity, particularly during the 19th century gold rush when miners sought durable clothing, the demand for high-quality indigo dye surged. Companies began to specialize in indigo dye production, leading to innovations in dyeing techniques. Today, manufacturers utilize advanced methods like discharge dyeing and rope dyeing, which enhance the richness and depth of the color. These processes not only ensure the fabric retains its vibrant hue after washing but also provide a unique worn-in look that is so coveted in modern fashion.
In recent years, the rise of sustainable and eco-friendly practices has received significant attention in the indigo dye industry. Traditional dyeing methods often involve the use of toxic chemicals, leading many manufacturers to explore natural and organic alternatives. Plant-based indigo, bio-based dyes, and innovative sustainable practices are becoming more mainstream, catering to the environmentally conscious consumer.
Today, denim brands are increasingly transparent about their sourcing and dyeing practices, acknowledging their role in the global textile industry. In an era where sustainability holds immense value, the path of indigo dye continues to evolve, intertwining history with modern ethics.
As we look to the future, it is clear that indigo, an age-old dye, remains relevant. It captures the essence of fashion, tradition, and sustainability, promising to be an enduring presence in textiles for years to come. The journey of indigo dye is not just about color; it’s a reflection of cultural heritage, innovation, and the quest for a more sustainable fashion industry.
-
The Timeless Art of Denim Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Rise of Sulfur Dyed Denim
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Rich Revival of the Best Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Enduring Strength of Sulphur Black
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Ancient Art of Chinese Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Industry Power of Indigo
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Black Sulfur is Leading the Next Wave
NewsJul.01,2025

Sulphur Black
1.Name: sulphur black; Sulfur Black; Sulphur Black 1;
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C6H4N2O5
4.CAS No.: 1326-82-5
5.HS code: 32041911
6.Product specification:Appearance:black phosphorus flakes; black liquid

Bromo Indigo; Vat Bromo-Indigo; C.I.Vat Blue 5
1.Name: Bromo indigo; Vat bromo-indigo; C.I.Vat blue 5;
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C16H6Br4N2O2
4.CAS No.: 2475-31-2
5.HS code: 3204151000 6.Major usage and instruction: Be mainly used to dye cotton fabrics.

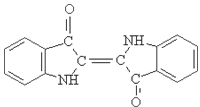
Indigo Blue Vat Blue
1.Name: indigo blue,vat blue 1,
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C16H10N2O2
4.. CAS No.: 482-89-3
5.Molecule weight: 262.62
6.HS code: 3204151000
7.Major usage and instruction: Be mainly used to dye cotton fabrics.

