Natural Indigo Dyeing Techniques and Leading Manufacturers in the Textile Industry
The Rise of Natural Indigo Fabric Dye Manufacturers A Sustainable Revolution in Fashion
In recent years, the fashion industry has witnessed a significant shift towards sustainable practices. Among these, the use of natural dyes has emerged as a noteworthy trend, with indigo dye leading the charge. Known for its vibrant blue hue and rich cultural heritage, natural indigo dye has captivated the hearts of designers, textile manufacturers, and environmentally conscious consumers alike. This article delves into the role of natural indigo fabric dye manufacturers in promoting sustainability and craftsmanship within the textile industry.
The Significance of Indigo Dye
Indigo dye, derived from the leaves of the indigo plant (genus Indigofera), has been used for centuries across various cultures. Its deep blue shade has adorned garments from ancient Egypt to the traditional textiles of India and Japan. Unlike synthetic dyes, which can contain harmful chemicals and contribute to water pollution, natural indigo is biodegradable and poses fewer risks to human health and the environment. As consumers become more aware of the environmental impact of their choices, the demand for natural indigo dye is on the rise.
The Role of Manufacturers
Natural indigo fabric dye manufacturers play a crucial role in the sustainable fashion ecosystem. They not only produce the dye but also hold the knowledge and expertise to create high-quality textiles that meet the growing demand for eco-friendly products. By sourcing indigo plants responsibly and utilizing traditional dyeing techniques, these manufacturers help revive age-old practices while ensuring that their production processes are environmentally friendly.
One notable example is the resurgence of shibori dyeing techniques in Japan, which utilize natural indigo to create stunning patterns on fabric. Manufacturers are increasingly embracing such artisanal methods, appealing to consumers who value handcrafted products. By fostering collaborations with artisans, these companies help preserve cultural heritage while promoting sustainability in the global market.
Challenges Faced by Natural Indigo Manufacturers
Despite the growing interest in natural indigo, manufacturers face several challenges in their pursuit of sustainability. The cultivation of indigo plants requires specific climatic conditions, and the farming of these crops is often labor-intensive. Additionally, competition with synthetic dyes, which are cheaper and more readily available, poses a significant obstacle for natural dye producers.
natural indigo fabric dye manufacturers
Moreover, the production of natural indigo can be less predictable in terms of color consistency and yield, which can affect manufacturers’ ability to meet market demands. To address these challenges, manufacturers are investing in research and development to improve cultivation practices and enhance dye stability. By focusing on innovation, they aim to create a more sustainable supply chain that benefits both producers and consumers.
Economic and Environmental Benefits
Supporting natural indigo fabric dye manufacturers not only contributes to environmental sustainability but also stimulates local economies. Many of these manufacturers work closely with farmers and artisans, providing fair wages and sustainable livelihoods. The promotion of natural dyeing practices can lead to job creation in rural areas, helping to uplift communities that rely on traditional craftsmanship.
Furthermore, the environmental benefits of natural indigo dyeing are significant. The cultivation of indigo plants can contribute to soil health and biodiversity, as these plants are often grown in rotational systems that enhance agricultural sustainability. Natural dyes also reduce water pollution, as they do not require the harsh chemicals associated with synthetic dyeing processes.
The Future of Natural Indigo Dyeing
As consumers continue to seek out sustainable options, the future of natural indigo fabric dye manufacturers looks promising. Brands are increasingly incorporating natural dyes into their collections, offering consumers stylish yet eco-friendly alternatives. Additionally, the rise of online marketplaces and sustainable fashion platforms has enhanced visibility for these manufacturers, allowing them to connect with a broader audience.
Educational initiatives are also gaining momentum, as workshops and courses on natural dyeing techniques are being offered around the globe. Through these efforts, manufacturers not only share their expertise but also inspire a new generation of designers and consumers to value sustainability in fashion.
Conclusion
Natural indigo fabric dye manufacturers are at the forefront of a sustainable revolution in the textile industry. By embracing heritage techniques and prioritizing environmental responsibility, they are reshaping the future of fashion. As the demand for sustainable practices continues to grow, these manufacturers will play an integral role in creating a more eco-conscious and ethically produced textile landscape. Through their efforts, the beautiful tradition of natural indigo dyeing will continue to thrive, offering a vibrant alternative to conventional dyeing methods for generations to come.
-
The Timeless Art of Denim Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Rise of Sulfur Dyed Denim
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Rich Revival of the Best Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Enduring Strength of Sulphur Black
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Ancient Art of Chinese Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Industry Power of Indigo
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Black Sulfur is Leading the Next Wave
NewsJul.01,2025

Sulphur Black
1.Name: sulphur black; Sulfur Black; Sulphur Black 1;
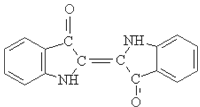
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C6H4N2O5
4.CAS No.: 1326-82-5
5.HS code: 32041911
6.Product specification:Appearance:black phosphorus flakes; black liquid

Bromo Indigo; Vat Bromo-Indigo; C.I.Vat Blue 5
1.Name: Bromo indigo; Vat bromo-indigo; C.I.Vat blue 5;
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C16H6Br4N2O2
4.CAS No.: 2475-31-2
5.HS code: 3204151000 6.Major usage and instruction: Be mainly used to dye cotton fabrics.

Indigo Blue Vat Blue
1.Name: indigo blue,vat blue 1,
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C16H10N2O2
4.. CAS No.: 482-89-3
5.Molecule weight: 262.62
6.HS code: 3204151000
7.Major usage and instruction: Be mainly used to dye cotton fabrics.

