Exploring the Benefits and Uses of Indigo Products in Various Sectors
Understanding VAT and Indigo Products An Insightful Overview
In today's global economy, the interplay between taxation and trade plays a critical role in shaping markets and influencing consumer behavior. One such aspect of taxation that has gained considerable attention over the years is Value Added Tax (VAT). Among various goods that may be subject to VAT, indigo products—particularly those derived from the natural dye indigo—offer a fascinating case study. This article will explore the significance of VAT in the context of indigo products, highlighting their cultural and economic relevance.
Understanding VAT and Indigo Products An Insightful Overview
With the rising popularity of these products, understanding the VAT implications becomes essential for both producers and consumers. VAT is a consumption tax levied on the value added at each stage of production and distribution. For businesses dealing in indigo products, especially those exporting or selling to international markets, clarity on VAT is crucial. Depending on the country, VAT rates may vary significantly, affecting pricing strategies, profit margins, and overall competitiveness in the marketplace.
vat indigo products
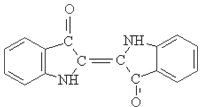
In many countries, indigo products, whether in the form of textiles, clothing, or artistic goods, can be either taxable or exempt from VAT. For instance, in the European Union, the VAT rates on textiles may range from 5% to 27%, depending on the member state. Producers need to be aware of the specific regulations governing indigo products in their respective countries to ensure compliance. This includes understanding potential exemptions or reduced rates applicable to artisans and small businesses that produce traditionally crafted goods.
From a consumer standpoint, VAT can affect purchasing decisions. The inclusion of VAT in the final price of indigo products can deter purchases if the cost becomes prohibitive. However, many consumers today are willing to pay a little extra for products that emphasize sustainability, ethical production, and cultural heritage. Thus, while VAT adds a layer of complexity to pricing, it can also position indigo products favorably in a market that values authenticity and environmental responsibility.
Moreover, the craft industry surrounding indigo products plays a vital role in providing livelihoods to artisans, particularly in developing countries. By framing VAT in a way that supports small-scale production and sustainable practices, governments can foster an environment where both local economies and traditional art forms thrive.
In conclusion, the intersection of VAT and indigo products elucidates a broader narrative about trade, culture, and sustainability. As the demand for natural and ethically sourced products continues to grow, understanding the implications of VAT becomes increasingly important for businesses and consumers alike. By navigating these complexities thoughtfully, stakeholders can contribute to a market that values both economic viability and cultural richness.
-
The Timeless Art of Denim Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Rise of Sulfur Dyed Denim
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Rich Revival of the Best Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Enduring Strength of Sulphur Black
NewsJul.01,2025
-
The Ancient Art of Chinese Indigo Dye
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Industry Power of Indigo
NewsJul.01,2025
-
Black Sulfur is Leading the Next Wave
NewsJul.01,2025

Sulphur Black
1.Name: sulphur black; Sulfur Black; Sulphur Black 1;
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C6H4N2O5
4.CAS No.: 1326-82-5
5.HS code: 32041911
6.Product specification:Appearance:black phosphorus flakes; black liquid

Bromo Indigo; Vat Bromo-Indigo; C.I.Vat Blue 5
1.Name: Bromo indigo; Vat bromo-indigo; C.I.Vat blue 5;
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C16H6Br4N2O2
4.CAS No.: 2475-31-2
5.HS code: 3204151000 6.Major usage and instruction: Be mainly used to dye cotton fabrics.

Indigo Blue Vat Blue
1.Name: indigo blue,vat blue 1,
2.Structure formula:
3.Molecule formula: C16H10N2O2
4.. CAS No.: 482-89-3
5.Molecule weight: 262.62
6.HS code: 3204151000
7.Major usage and instruction: Be mainly used to dye cotton fabrics.

